The Forkhead box m1 (Foxm1) gene is crucial for G(1)/S transition and essential for mitotic progression. However, the transcriptional mechanisms downstream of FoxM1 that management these cell cycle occasions stay to be decided.
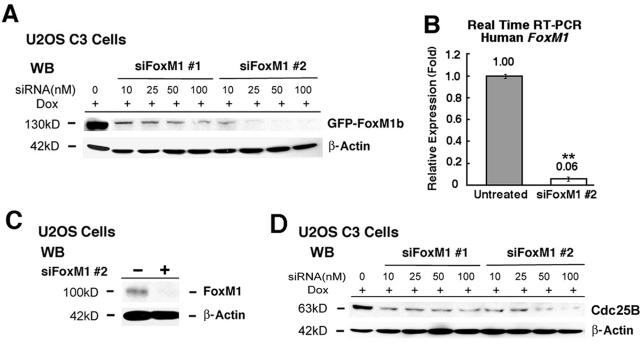
Here, we present that each early-passage Foxm1(-)(/)(-) mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) and human osteosarcoma U2OS cells depleted of FoxM1 protein by small interfering RNA fail to develop in tradition because of a mitotic block and accumulate nuclear ranges of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor (CDKI) proteins p21(Cip1) and p27(Kip1).
Using quantitative chromatin immunoprecipitation and expression assays, we present that FoxM1 is essential for transcription of the mitotic regulatory genes Cdc25B, Aurora B kinase, survivin, centromere protein A (CENPA), and CENPB. We additionally establish the mechanism by which FoxM1 deficiency causes elevated nuclear ranges of the CDKI proteins p21(Cip1) and p27(Kip1).
We present proof that FoxM1 is essential for transcription of Skp2 and Cks1, that are specificity subunits of the Skp1–Cullin 1-F-box (SCF) ubiquitin ligase advanced that targets these CDKI proteins for degradation throughout the G(1)/S transition. Moreover, early-passage Foxm1(-)(/)(-) MEFs show untimely senescence as evidenced by excessive expression of the senescence-associated beta-galactosidase, p19(ARF), and p16(INK4A) proteins.
Taken collectively, these outcomes exhibit that FoxM1 regulates transcription of cell cycle genes crucial for progression into S-phase and mitosis. Adaptive modifications to oxygen availability are crucial for cell survival and tissue homeostasis. Prolonged oxygen deprivation because of decreased blood stream to cardiac or peripheral tissues can result in myocardial infarction and peripheral vascular illness, respectively.
Mammalian cells reply to hypoxia by modulating oxygen-sensing transducers that stabilize the transcription issue hypoxia-inducible issue 1α (HIF-1α), which transactivates genes governing angiogenesis and metabolic pathways.
Oxygen-dependent modifications in HIF-1α ranges are regulated by proline hydroxylation and proteasomal degradation. Here we offer proof for what we imagine is a novel mechanism regulating HIF-1α ranges in remoted human ECs throughout hypoxia. Hypoxia differentially elevated microRNA-424 (miR-424) ranges in ECs.
miR-424 focused cullin 2 (CUL2), a scaffolding protein crucial to the meeting of the ubiquitin ligase system, thereby stabilizing HIF-α isoforms. Hypoxia-induced miR-424 was regulated by PU.1-dependent transactivation.
PU.1 ranges had been elevated in hypoxic endothelium by RUNX-1 and C/EBPα. Furthermore, miR-424 promoted angiogenesis in vitro and in mice, which was blocked by a selected morpholino. The rodent homolog of human miR-424, mu-miR-322, was considerably upregulated in parallel with HIF-1α in experimental fashions of ischemia. These outcomes recommend that miR-322/424 performs an necessary physiological position in post-ischemic vascular transforming and angiogenesis.
Identification of the von Hippel-lindau tumor-suppressor protein as half of an energetic E3 ubiquitin ligase advanced
Mutations of von Hippel-Lindau illness (VHL) tumor-suppressor gene product (pVHL) are present in sufferers with dominant inherited VHL syndrome and in the overwhelming majority of sporadic clear cell renal carcinomas.
The operate of the pVHL protein has not been clarified. pVHL has been proven to kind a fancy with elongin B and elongin C (VBC) and with cullin (CUL)-2. In gentle of the structural analogy of VBC-CUL-2 to SKP1-CUL-1-F-box ubiquitin ligases, the ubiquitin ligase exercise of VBC-CUL-2 was examined on this examine.
We present that VBC-CUL-2 reveals ubiquitin ligase exercise, and we recognized UbcH5a, b, and c, however not CDC34, as the ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes of the VBC-CUL-2 ubiquitin ligase. The protein Rbx1/ROC1 enhances ligase exercise of VBC-CUL-2 because it does in the SKP1-CUL-1-F-box protein ligase advanced.
We additionally discovered that pVHL associates with two proteins, p100 and p220, which migrate at an identical molecular weight as two main bands in the ubiquitination assay. Furthermore, naturally occurring pVHL missense mutations, together with mutants succesful of forming a fancy with elongin B-elongin C-CUL-2, fail to affiliate with p100 and p220 and can not exhibit the E3 ligase exercise. These outcomes recommend that pVHL is perhaps the substrate recognition subunit of the VBC-CUL-2 E3 ligase.
This can be, to our data, the first instance of a human tumor-suppressor protein being straight concerned in the ubiquitin conjugation system which ends up in the focused degradation of substrate proteins.
The inactivation of the von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) gene predisposes affected people to VHL syndrome and is an early genetic occasion related to sporadic renal cell carcinoma and CNS hemangioblastomas. The VHL protein (pVHL) has been proven to kind a steady advanced with elongin B and elongin C, two components that stabilize and activate the transcription elongation issue elongin A.
Here, Hs-CUL-2, a member of the just lately recognized multigene household, the cullins, is proven to particularly affiliate with the trimeric pVHL-elongin B-C (VBC) advanced in vitro and in vivo. Nearly 70% of naturally occurring cancer-predisposing mutations of VHL disrupt this interplay. The pVHL-Hs-CUL-2 affiliation is strictly depending on the integrity of the trimeric VBC advanced.
Immunofluorescence research present Hs-CUL-2 to be a cytosolic protein that may be translocated to the nucleus by pVHL. Recently it has been proven {that a} yeast Hs-CUL-2 homolog, Cdc53, is a component of a ubiquitin protein ligase advanced that targets cell cycle proteins for degradation by the ubiquitin proteolytic pathway.
In Caenorhabditis elegans, a null mutation of one other Hs-cul-2 homolog, Ce-cul-1, ends in hyperplasia in all tissues and is required for cell cycle exit. Hence, Hs-cul-2 could also be required for VHL operate and, subsequently, could also be a candidate human tumor-suppressor gene.