Tumor-derived proteins could happen within the circulation in consequence of secretion, shedding from the cell floor, or cell turnover. We have utilized an in-depth complete proteomic technique to plasma from intestinal tumor-bearing Apc mutant mice to determine proteins associated with tumor improvement.
We used quantitative tandem mass spectrometry of fractionated mouse plasma to determine differentially expressed proteins in plasma from intestinal tumor-bearing Apc mutant mice relative to matched controls. Up-regulated proteins had been assessed for the expression of corresponding genes in tumor tissue.
A subset of proteins implicated in colorectal most cancers had been chosen for additional analysis on the tissue stage utilizing antibody microarrays, Western blotting, tumor immunohistochemistry, and novel fluorescent imaging. We recognized 51proteins that had been elevated in plasma with concordant up-regulation on the RNA stage in tumor tissue.
The record included a number of proteins concerned in colon most cancers pathogenesis: cathepsin B and cathepsin D, cullin1, Parkinson illness 7, muscle pyruvate kinase, and Ran. Of these, Parkinson illness 7, muscle pyruvate kinase, and Ran had been additionally discovered to be up-regulated in human colon adenoma samples. We have recognized proteins with direct relevance to colorectal carcinogenesis which can be current each in plasma and in tumor tissue in intestinal tumor-bearing mice. Our outcomes present that built-in analysis of the plasma proteome and tumor transcriptome of genetically engineered mouse fashions is a strong method for the identification of tumor-related plasma proteins.
NUP98 dysregulation in myeloid leukemogenesis
Nucleoporin 98 (NUP98) is a element of the nuclear pore complicated that facilitates mRNA export from the nucleus. It is mapped to 11p15.5 and is fused to a quantity of distinct companions, together with 9 members of the homeobox household as a consequence of leukemia-associated chromosomal translocations.
NUP98-HOXA9 is associated with the t(7;11)(p15;p15) translocation in acute myeloid leukemia (AML), myelodysplastic syndrome, and blastic disaster of continual myeloid leukemia. Expression of NUP98-HOXA9 in murine bone marrow resulted in a myeloproliferative illness progressing to AML by 7-Eight months.
Transduction of NUP98 fusion genes into human CD34(+) cells confers a proliferative benefit in long-term cytokine-stimulated and stromal cocultures and in NOD-SCID engrafted mice, associated with a five- to eight-fold improve in hematopoietic stem cells. NUP98-HOXA9 expression inhibited erythroid and myeloid differentiation however enhanced serial progenitor replating. NUP98-HOXA9 upregulated a quantity of homeobox genes of the A and B cluster in addition to MEIS1 and Pim-1, and downmodulated globin genes and C/EBPalpha.
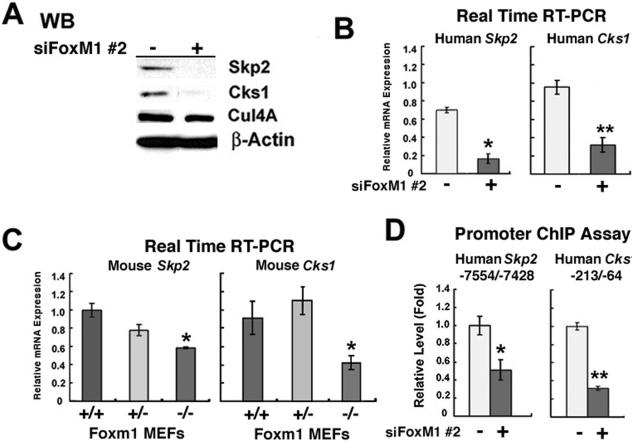
The HOXA9 element of the NUP98-HOXA9 fusion protein was shielded from cullin-4A-mediated ubiquitination and subsequent proteasome-dependent degradation. In NUP98-HOX-transduced CD34(+) cells and cells from AML sufferers with t(7;11)(p15;p15) NUP98 was now not associated with the nuclear pore complicated however shaped intranuclear aggregation our bodies. Analysis of NUP98 allelic expression in AML and myelodysplastic syndrome confirmed loss of heterozygosity noticed in 29% of the previous and eight% of the latter. This was associated with poor prognosis.
Diversification of the cullin household
BACKGROUND
Cullins are proteins concerned in ubiquitination by means of their participation in multisubunit ubiquitin ligase complexes. In this examine, I take advantage of comparative genomic information to determine the sample of emergence and diversification of cullins in eukaryotes.
RESULTS
The accessible information point out that there have been three cullin genes earlier than the unikont/bikont cut up, which I’ve known as Culalpha, Culbeta and Culgamma. Fungal species have fairly strictly conserved these three ancestral genes, with solely occasional lineage-specific duplications. On the opposite, a number of extra genes appeared within the animal or plant lineages. For instance, the human genes Cul1, Cul2, Cul5, Cul7 and Parc all derive from the ancestral Culalpha gene. These outcomes, collectively with the accessible purposeful information, counsel that three differing kinds of ubiquitin ligase cullin-containing complexes had been already current in early eukaryotic evolution: 1) SCF-like complexes with Culalpha proteins; 2) Culbeta/BTB complexes; and, 3) Complexes containing Culgamma and DDB1-like proteins. Complexes containing elongins have arisen extra not too long ago and maybe twice independently in animals and fungi.
CONCLUSIONS
Most of the identified varieties of cullin-containing ubiquitin ligase complexes are historic. The accessible information counsel that, for the reason that origin of eukaryotes, complicated variety has been largely generated by combining intently associated subunits, whereas radical improvements, giving rise to novel varieties of complexes, have been scarce. However, a number of protist teams not examined up to now comprise extremely divergent cullins, indicating that extra varieties of complexes could exist.